- Joined
- 31.10.19
- Messages
- 378
- Reaction score
- 833
- Points
- 93

An antidetect browser replaces or disguises the digital fingerprint of the browser that websites use to identify users. Websites capture the digital fingerprint to identify users engaged in multi-accounting - managing multiple accounts from a single device. Multi-accounting is prohibited on certain social networks, advertising platforms, betting sites, etc.
How do websites detect multi-accounting?
- By IP: Websites block suspicious addresses and prohibit creating multiple accounts from a single address.
- By behavior: If a user interacts with a site in a non-standard or strange way, they may receive a warning, captcha or ban. For example, on an advertising platform like Facebook, posting multiple ads in succession may be considered suspicious due to common practices of scammers who hack accounts and run numerous ads through them.
- By a unique set of user device information known as the digital fingerprint.
What is a fingerprint?
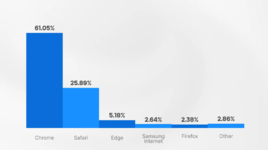
A fingerprint consists of various characteristics of the user's hardware and browser. Each of these characteristics can be common; for example, there are many users with Windows 11 OS, Chrome browser, and a screen resolution of 1920x1080. By adding 30-40 more parameters for verification, a user's uniqueness can be determined with high probability.
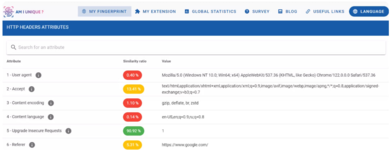
Checkers like AmIUnique compare your fingerprint with others based on several parameters to assess the likelihood of your fingerprint being unique.
How do anti-detection tools help bypass restrictions?
Let's discuss how antidetect allows circumventing site protection against multi-accounting, using Octo Browser as an example. To avoid raising suspicions, users should appear unremarkable to anti-fraud systems. Octo Browser uses the Chromium platform, also the foundation for over thirty other popular browsers, including the market leader, Google Chrome. Extra tracking mechanisms of Google are removed from Chrome in Octo, such as RLZ, histograms, UMA metrics, and Chrome features tied to Google services like synchronization and cloud password management. The browser is based on a Google Chrome-free version of Chromium, closely resembling Chrome from the site's perspective. To prevent antidetect profiles from being exposed during Chrome updates, developers update their browsers. Octo updates within a few days of each Chrome release.
High-quality fingerprint substitution ensures that a website cannot obtain genuine information about the device or browser unless authorized by the user. The information received by the security system should be consistent, meaning the facts should not contradict each other. For instance, if your OS is identified as MacOS while your system fonts are Windows-based it could lead to a ban. Security systems use various methods to check fingerprints, from requesting User-agent to analyzing device hardware fingerprints like Canvas and WebGL. These unique features are derived from the browser's rendering of a hidden image on the page, generating a lengthy hash used for identification. Checkers are used to verify if there are any leaks of real information from the antidetect browser. There are many checkers, each with slightly different working principles. Popular ones include Browserleaks, PixelScan, and Whoer.
In addition to fingerprint substitution, an antidetect browser should also provide the capability to conveniently manage multiple accounts. In the case of Octo, developers have integrated all the necessary functionality for anti-detection into a stripped-down version of Chrome. This includes the ability to create and manage browser profiles, each of which can be customized with its own fingerprint settings. Another must-have feature is the ability to connect proxies to each profile. It's essential to use high-quality proxies because they are responsible for changing your IP address. If your proxies are flagged in a database of untrustworthy sources, then no anti-detection measures will prevent you from being banned.
The browser is optimized for running a large number of profiles, with tools for automation via APIs. There are also tools for teamwork, cookie management, video stream substitution, manual input simulation and much more. All of this allows users to utilize their profiles for different services or sites, ensuring that no tracking scripts can link visits or actions history between different profiles. Often among the capabilities of antidetects you may encounter special tools for working with FB and Google, no-code automation and many other features. These features enhance the anti-detection experience without compromising the quality of fingerprint substitution.
Conclusion.
Developing an antidetect browser is an ongoing process. The security systems of the website are developing, Chrome are regularly updated, and the user needs are changed. Therefore, developers focus on maintaining the browser's technical state, ensuring stability, and delivering high-quality updates. For Octo, the service availability stands at 99.995% with frequent updates that undergo thorough testing. In summary, antdetect browsers play a crucial role in circumventing site protection measures, primarily by substituting unique user fingerprints and providing tools for managing multiple accounts effectively.
Last edited: