- Joined
- 31.10.19
- Messages
- 378
- Reaction score
- 833
- Points
- 93
A seemingly ordinary file or photo sent to a friend may contain information that the sender didn't intend to share at all. So a photo with a kitty, in addition to the information contained in the picture, can tell the recipient about where and when it was taken and even from what device. The same applies to social networks - a photo uploaded to the Internet contains information that can not only compromise the user but also tell, for example, about his location. In addition, online purchases and other online activities leave such digital footprints. But not everyone knows what file metadata is today. In this article we will tell you what are the dangers of file metadata, how to protect them and remove unwanted information contained in sent photos and other files.
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) - is additional information encrypted in the photo which allows you to find out a lot of details from a regular photo: from the camera it was taken with to the focal length. As a rule, photographers use them to repeat successful photos: it's enough to set the right values, rather than trying to "play" with the camera settings. EXIF data exist not only inside graphic files. It can be found in videos, documents, music, etc. It's assigned automatically when the file is created.

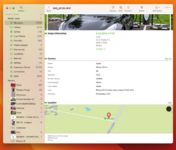
An example of displaying EXIF metadata in the Exif Pilot app.
The Danger of Metadata.
The first thing that metadata gives is the ability to set license restrictions and identify the author. They also help websites and apps organize and identify content. And, for example, telecom operators can track user activity on certain resources. Any targeting, segmentation of the target audience by preferences, location, habits, field of activity is the result of the analysis of user metadata or rather digital traces that they left on social networks and on the Internet as a whole. With the help of metadata, marketers can find out not only the model of your smartphone but also frighteningly accurate queries.
Everything we do online: send photos, files, publish posts, create music selections, make purchases and so on, in addition to the declared information, leaves behind us the so-called digital footprints. They are formed precisely due to metadata. Often, especially by ordinary people, this fact is ignored and with it the threat of illegal actions grows. By studying, for example, photos on social networks the offender can build a standard route for the victim as well as find out his favorite places and preferences. Based on this data, you can prepare a phishing attack or use a social engineering method.
It should not be forgotten that the threat of metadata falling into the hands of cybercriminals for companies is no less or even greater than for ordinary users. Often metadata can help criminals decrypt stolen information. So, not understanding from the contents of the file what exactly it's about and how it can be used cybercriminals turn to metadata which makes it possible to quickly deal with stolen goods and sell them. Or, for example, criminals can use meta-information to find out what software is installed in the organization and prepare a more accurate attack based on this.

For Linux, there's a program Metadata Cleaner - that allows you to remove metadata from different types of files:

For Android, you can use Scrambled Exif - the simplest program to completely remove all metadata from photos.
For IOS, try Metapho - is an app that allows you to view and manage photo metadata.
You can remove metadata using apps, online tools, basic device settings and settings when uploading. But don't forget that metadata can be useful, especially when it comes to work moments. For example, metadata can help determine in which editor and software the file was created, it's working name and the date it was created. This can provide an opportunity to convert the file or use it on a new system. In addition, even an ordinary user needs to remember where and when a file was created or a photo was taken. But don't forget that in the absence of metadata protection the same information can be obtained by an attacker and used against you. For example, finding out the software version and other details about the devices used by the company will be very useful when selecting cyberattack tools.
What is EXIF metadata?
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) - is additional information encrypted in the photo which allows you to find out a lot of details from a regular photo: from the camera it was taken with to the focal length. As a rule, photographers use them to repeat successful photos: it's enough to set the right values, rather than trying to "play" with the camera settings. EXIF data exist not only inside graphic files. It can be found in videos, documents, music, etc. It's assigned automatically when the file is created.
File metadata includes:
- Camera model
- Date and exact time of shooting
- Information about the copyright
- ISO light sensitivity values
- Camera sensor size
- Photo orientation
- Aperture settings
- Frame thumbnail
- Frame resolution
- Geometry
- etc.

An example of displaying EXIF metadata in the Exif Pilot app.
The Danger of Metadata.
Everything we do online: send photos, files, publish posts, create music selections, make purchases and so on, in addition to the declared information, leaves behind us the so-called digital footprints. They are formed precisely due to metadata. Often, especially by ordinary people, this fact is ignored and with it the threat of illegal actions grows. By studying, for example, photos on social networks the offender can build a standard route for the victim as well as find out his favorite places and preferences. Based on this data, you can prepare a phishing attack or use a social engineering method.
It should not be forgotten that the threat of metadata falling into the hands of cybercriminals for companies is no less or even greater than for ordinary users. Often metadata can help criminals decrypt stolen information. So, not understanding from the contents of the file what exactly it's about and how it can be used cybercriminals turn to metadata which makes it possible to quickly deal with stolen goods and sell them. Or, for example, criminals can use meta-information to find out what software is installed in the organization and prepare a more accurate attack based on this.
How to see EXIF?
The metadata cannot be seen directly in the file itself - you need to open the context menu and go to the properties section.
- Browsers: Metadata can also be viewed online using the Exif Viewer extension (available for Google Chrome and Mozilla users).
- Windows: Right-click on the file, select "Properties" - "Details". The window that opens will contain the metadata of the photo.
- Android: On your smartphone or tablet you need to open the Google Photos app. The EXIF data will be located under the "i" icon.
- MAC: Click to select the file, then press "Command + I". The "EXIF" tab will contain the data you need.
How to delete?
For Windows, you can use EXIF Purge - a small portable application to remove metadata from multiple images at once.

For Linux, there's a program Metadata Cleaner - that allows you to remove metadata from different types of files:

For Android, you can use Scrambled Exif - the simplest program to completely remove all metadata from photos.
For IOS, try Metapho - is an app that allows you to view and manage photo metadata.
You can remove metadata using apps, online tools, basic device settings and settings when uploading. But don't forget that metadata can be useful, especially when it comes to work moments. For example, metadata can help determine in which editor and software the file was created, it's working name and the date it was created. This can provide an opportunity to convert the file or use it on a new system. In addition, even an ordinary user needs to remember where and when a file was created or a photo was taken. But don't forget that in the absence of metadata protection the same information can be obtained by an attacker and used against you. For example, finding out the software version and other details about the devices used by the company will be very useful when selecting cyberattack tools.
Last edited: