- Joined
- 31.10.19
- Messages
- 863
- Reaction score
- 1,849
- Points
- 93
RAT
RAT is a remote access tool that allows full access to a system and, in some cases, even administrative rights, which in turn opens up any possibilities for a hacker's work. By the way, viruses are also divided into those that require a server and those that work autonomously. So, for RAT, a server is needed in 99% of cases. The server here doesn't always mean a dedicated server that will run 24/7. It can also be the hacker's computer, which will run the client only as needed. For RAT to work, a static (permanent) IP address is required or dynamic (instant) DNS change when the IP address changes.
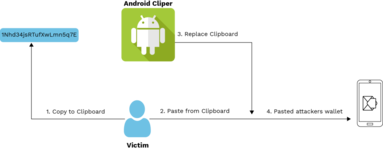
Clippers are simple in nature but serious in terms of threat effectiveness software that substitutes data from your clipboard when making cryptocurrency (and not only) transactions. The trick is that almost no one manually types the wallet address when making a deal. For this reason, hackers use the pattern of the required currency wallet to replace the copied wallet in the clipboard with their own.
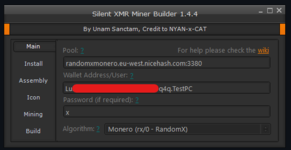
Why buy expensive equipment, rent space, and pay for electricity when you can run everything on someone else's computers? A miner is a program whose goal is to convert the power of your computer into digital assets in the hacker's wallets. Often, they are installed by negligent system administrators on computers in state educational institutions (due to the use of cracked software) and even computer club managers do not shy away from this; their goal is to monetize devices that are idle during free (and not only) time.
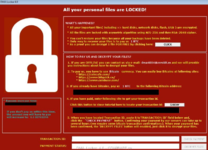
Why get paid for the resources of devices when the most valuable thing you can find on a "victim's" computer is information? For large companies, it can be worth thousands to millions of dollars. By the way, one of the major hacker groups REvil, which operated on this scheme, was recently apprehended in Russia and faces significant consequences. The principle of operation is to complicate or completely remove the owner's access to the information stored on their hard drive and demand money for the return of access. However, as practice shows, this happens only in 33% of cases. Another 33% is for the fact that it cannot be restored even after payment. The remaining 33% is for the fact that they simply do not want to restore it.
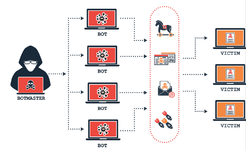
Botnets are centralized networks of computers (and other devices) whose task is to work together. This can be for mining and DDoS attacks, as well as more perverse forms of use. DDoS is used for denial of service attacks on servers, as the name "distributed denial of service" suggests. There is protection against this, but within very specific limits. The number of devices in the botnet determines its power.
A keylogger records text from the keyboard during input, often sending it to the hacker's server. Currently, they are not particularly dangerous for users, as all services have long been using two-factor, if not three-factor, authentication. Occasionally, and for a very narrow range of targets, they can be useful in hacking tasks as an additional tool.
Stealers are the most relevant malware. They target ordinary people who have +/- valuable information on their computers (especially in browsers), as well as those with accounts on Instagram, Telegram, Steam, Discord and others. Accounts are instantly sold for other tasks, such as spam mailings or crypto streams. Stealers can be bundled with other malware and have a huge database of detections, as the same software is widely used, which is constantly re-encrypted and reintroduced to victims.
HVNC
HVNC is an advanced system that is extremely dangerous and very easy to use. You are unlikely to find it by clicking the first link on Google. The principle of HVNC is to gain hidden remote access for the attacker to your computer. It's often used by hackers for "cleaning out" (withdrawing money from your PayPal wallet). The developers of such tools are punished and imprisoned even before they reach mass distribution and their price on hacker forums is very high. After all, when using it, the attacker is essentially behind your computer.
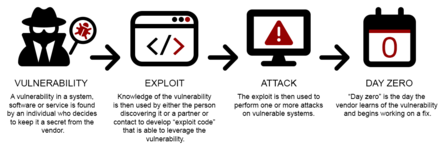
0-day is not a virus, but it's definitely worth mentioning. These are vulnerabilities that are not known even to the software developers themselves. They are sold for very high prices on hacker forums. These vulnerabilities in the code can cause enormous problems for all users of the software in which they are found. For example, it could be a vulnerability in "Windows Defender" that allows a hacker to silently install malware. The level of threat varies greatly; it could be a simple bypass of antivirus protection or the ability to install a backdoor.